Technical SEO: The Ultimate Guide for 2022
- Guest Author: Frank Robertson
- , Last Updated: July 27, 2024
This is the ultimate guide to Technical SEO this year.
In the expert-written guide, you will learn
- What is Technical SEO
- Why is it important
- Website structure
- How to improve pagespeed
- Much more
So, If you want your website to be technically better, this technical SEO guide will definitely solve your problems.
Let’s solve the technical SEO problems.

Technical SEO: The Ultimate Guide
What is search engine optimization?
SEO which stands for search engine optimization is a set of strategies that improve the ranking of websites on the search engine result page (SERP).
This is achievable through different SEO techniques that are done on or off your website. Strategies like Technical SEO, On-page SEO, and off-page are the three components of SEO.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is all about improving the technical side of any website to increase its ranking in the search engines like Google and Bing.
Technical SEO is part of on-page SEO services that work together to enhance the performance of different elements on your website to make it rank higher on the search engines.
Anything done outside of your website is considered off-page SEO. Activities on social media or more importantly getting other powerful sites to link back to your pages is an example of off-page SEO.
Is Technical SEO THAT Important?
The short answer is YES. Google policy is to provide the best possible results to the users’ inquiries. your website needs to be worthy in Google’s eyes so that it ranks higher in the SERP for users to click on it.
For that, you need to do a thorough Technical SEO. Faster load time, mobile responsiveness, security, free of duplicate content, and a plethora of other different steps need to be taken so that search engine robots find it easier to crawl, render and index your web pages.
What Can You Do to Improve Your Website’s Technical SEO
There are lots of techniques and strategies you can use to enhance a website’s technical SEO. Probably more than what an average site owner needs.
The list below is probably way more than most sites need to do in order to have a robust, well-optimized technical SEO website.
- JS (JavaScript)
- XML sitemap
- 404 pages
- 301 redirects
- Internal link structure
- Site structure
- Beautiful UI/UX design
- Security
- Data structure
- Thin and duplicated content
- URL structure
- Canonical tags
The list can go on and on about different techniques that are used but these strategies mentioned above are what you need to start with to work on your technical SEO.
Work on Your Website’s Structure and Navigation
![]()
Site structure is how effectively you arrange the content on your website for your visitors. Every website has a set of different pages that house written or visual content.
Site structure focuses on how these web pages and their contents are grouped and viewed by the users. A well-structured website will benefit both the users and your website; it will also help Google index your web pages easier.
Site structure is done through classifications tools, like categories and tags but also using internal links, navigation, and breadcrumbs.
Site structure should be prioritized even before crawling and indexing. Because many crawling and indexing problems stem from poorly designed site structures.
A messy site also would be difficult to manage especially over time as you post more content on the web. The logical and more natural first step would be doing your site structure first and do take it seriously.
1) Build a Flat Structure
Every site needs a structure that fits its content perfectly to make the users’ experience as smooth as possible. A flat site structure is a method where all your pages are a few links from your homepage.
A flat structure has other benefits as well. Google will find it easier to crawl and index all your pages because they are all linked together and lead to your homepage.
Another good point is that in this technique all your links are categorized under the related topics that are in the navigation bar which is located on the homepage. This will help the users and especially Google a lot.
2) Make sure your URL Structure Is Logical and Consistent
An average website can have about 10 to 30 pages on each page. There are a different number of internal and external links.
According to MOZ, every page can have about 100 links. Structuring all these links is a time-consuming task but very essential to your site structure and your Technical SEO.
The benefits of all these hassles are a better user experience. we know when the user is happy and clicking your semantically correct links, Google is happy too.
The second benefit is that when you structure your links to be semantically and readable for the users instead of letters and numbers, you can use your favorite keywords instead.
These keywords can help you rank better. Also writing a readable link structure brings more clicks because users will feel more comfortable knowing where the link is taking them.
The third benefit is that now you can use these well-readable links as anchor text in blogs, social media like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. And as we said above these links will bring more people to your website because the users will feel more comfortable clicking on them.
3) Breadcrumbs Navigation
Breadcrumbs are another navigational strategy that is used to enable users to track where they are on your website. They can be located at the top of your website or below the navigation bar.
It plays vital role in the technical SEO to help users to analyze the page.
It shows exactly where the user is on your site and if they need to go to a previous page or backtrack multiple pages, they can just click on it instead of going back one by one.
The image below is an example of a typical breadcrumbs navigation.
![]()
Watch Out for Thin and Duplicate Content
Thin content is the type of content that doesn’t offer the users any useful information and has little to no value. This type of content can hurt your SEO ranking so make sure your content is valuable and informative for your users.
Duplicated content as the name suggests is the same content on different pages. This is also not good and confuses Google.
If you take your content seriously and write unique, valuable, and specific content for every page on your website you don’t need to worry much about thin or duplicated content.
But every site can suffer from these problems especially if you have lots of content on your website. Next, we will discuss a set of tools that can aid you in identifying any duplicated or thin content on your website.
1) Use SEO Audit Tools to Check for Duplicate Content
There are lots of useful tools that can help you identify any duplicated content with a few simple steps. Copyscape and Screaming Frog are very useful in this regard.
On Copyscape, you can enter the website domain and let it do its magic. It will let you know in no time if or how many duplicated contents there are on your website.
The next tool, Screaming Frog crawls the web and gives you data like meta description, page title, duplicated content, and canonical elements for each URL you search for. It is the best option for new businesses because the free version offers you 500 URLs.
2) Noindex Pages That Are Not That Significant
Noindex, as obvious as it sounds, means that the webpage shouldn’t be indexed and listed in the search engine result page (SERP).
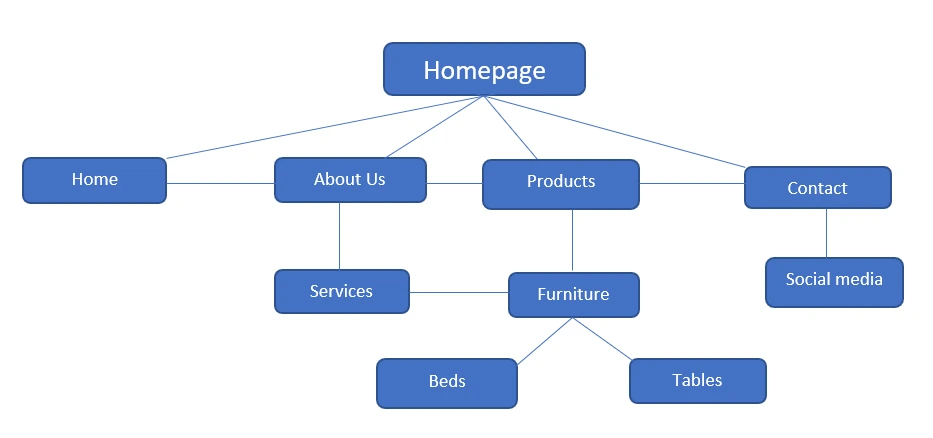
Make your pages load faster
We all love fast and snappy web pages. There’s nothing more awful than waiting for a page to load. That’s why slower pages have a higher bounce rate than faster pages.
On the other hand, fast pages will result in higher clicks and your users will stay longer on your site.
1) Choose the Right Hosting
The first step to having a faster site, in general, is choosing fast hosting. This is NOT the place to cut down on your budget.
It’s worth it to spend a little more to get the best and fastest hosting services available in your region.
Another important factor about site hosting that you need to take into consideration is the location of the server that you’re going to upload your website on.
Ideally, you want the server to be as close as it can be to the majority of your site visitors. Some hosting websites even provide different servers in different areas to make your site easily accessible for a variety of regions and users.
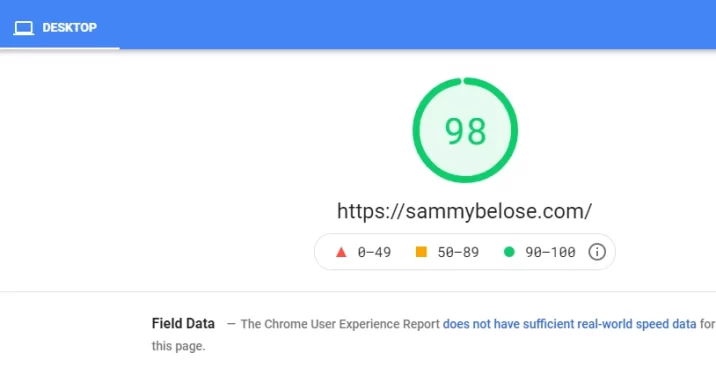
2) Cut Down on HTTP Requests
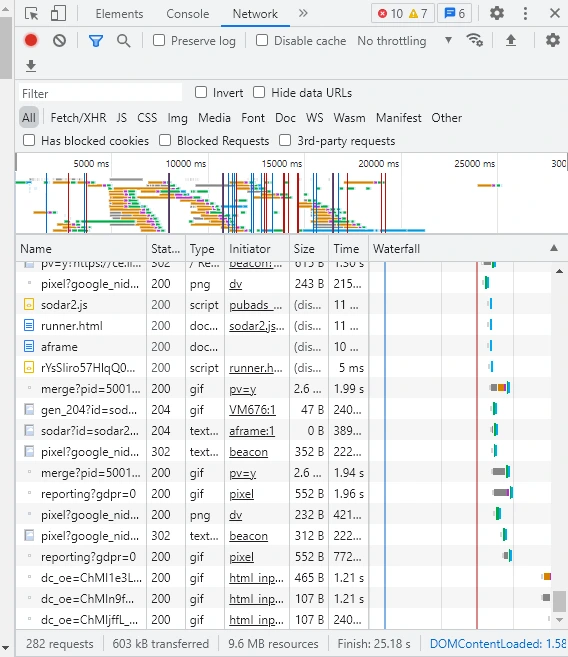
What are HTTP requests?
It’s when you visit a website on any browser. The browser will ask the server for that particular webpage’s files. Next, the browser will display the files for you inside a tab so you can interact with the website.
The fewer the files the less time it will take for the page to load. So in general we need to shrink down our HTTP requests for our pages to make them load faster.
You can use technical seo tools like Pingdom or GTmetrix to see how many HTTP requests your URLs generate. Or you can use Google chrome console. You can right-click on your desired page then click on inspect.
On the Google Chrome console navigate to “network” then press Ctrl+R. You will be presented with a list of all the requested HTTP. At the bottom of the page on your left, you can see the exact number of requests.
Your next step is to identify which requests are not necessary. Make sure you only have the essential requests.
Cut down on your image sizes, minify, and combine your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files. We will talk about these strategies in the next section of the article but it’s worth mentioning that you should never sacrifice the user experience over pagespeed.
3) Minify and combine files
Write clean CSS and HTML. Delete any spaces, commas, and unnecessary characters. Combine all of the CSS files into one.
Gzip is a suitable application to compress the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files that are more than 150 bytes. Remove any comments and unused codes to shrink down your files.
Google suggests using these apps for minifying your files which can lead to significant pagespeed posts inside your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files to reduce size.
For image files compression Use programs like photoshop because it gives you the ability to control the resolution of the image.
Crawling, Rendering, and Indexing
Google robots crawl the internet all the time to index new sites and web pages. This doesn’t mean they don’t need your help if you have poor technical SEO.
A good amount of your URLs will never be fully crawled and indexed. Don’t worry there are a set of tools available for you to determine which pages on your website aren’t crawled or indexed yet.
1) Use Tools to Identify Pages That Have Trouble Indexing
The first step any website owner needs to do is study the coverage report on Google search console.
Google search console page will provide you with an HTML file that you need to copy and paste into your original HTML file. To verify you’re the website owner.
This report lets you know which URLs on your website that Google has difficulty crawling and indexing.
2) Make Sure to Link to Deep Pages
Inside Google search console report, you will surely come across some deep pages that haven’t been indexed yet. You need to start linking to those pages inside your already indexed ones.
This will connect all your pages together and Google crawlers will find it easier to index your deep and forgotten web pages.
The next tool as mentioned above is Screaming Frog. This tool is very helpful in identifying the pages you want to index.
It can run all your website’s URLs and tells you which URL needs to be crawled and indexed. Use Google search console first because it’s a free and powerful tool. Screaming Frog is just to make sure 100% of your desired URLs are indexed.
3) Implement XML Sitemap
XML sitemap is one of the important technical SEO factor for indexing. It is a type of file that houses all your important pages for Google crawlers to find them faster. This file contains valuable information like when the page was last updated, how often that particular page changes.
It also aids search engines to understand your site structure better and determine which pages are more important for crawling and indexing.
Every site needs an XML sitemap. It shows how the structure of your site is important for you. You’d be surprised to see how many sites are out there that don’t bother with it.
By updating the sitemap regularly on your website, you allow search engines to know which URLs need to be crawled and indexed.
Conclusion:
Technical SEO is the crucial factor of SEO. If you perfectly optimize the website, you don’t have to work hard to rank any website.
I hope this guide will help you to solve problems on your website.
Now, I want to hear from you
What is your favorite Technical SEO Strategy?
Is it website architecture or optimizing pagespeed?
Please, let me know in the comment.
Frank Robertson
My name is Frank Robertson. I write about digital marketing and web development, especially if it’s intriguing and catches my attention. I currently work with a company in Melbourne that provides on-page SEO services.
![]Sammy-Belose_White-200x56-1.png](https://sammybelose.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/cropped-cropped-Sammy-Belose_White-200x56-1-1.png)
